Contact us at youthandpolitics0720@gmail.com or visit us at @youthnpolitics on instagram

Political Toolkit

The political toolkit is not your standard article but rather an encyclopaedia you can refer to for explanations of concepts or definitions of political terminology. Feel free to have it open while reading an article so you can quickly fill in some knowledge gaps!
Political Vocabulary II
Written By: Chesney Yim
Published By: Meredith Yuen

Political Titles and Positions
President
-
The head of government of a republic
-
Represent the country, pass and execute laws, and oversee the executive branch of the government
eg. Donald Trump of the United States, Emmanuel Macron of France
Vice President
-
The second-highest executive officer in a government
-
Often acts as the immediate successor to the president, sometimes overseeing the legislative branch
eg. JD Vance of the United States, Jagdeep Dhankhar of India
** Although many countries are headed by Presidents, many do not have VICE
presidents
Prime Minister
-
The head of government in parliamentary systems
-
Oversee the executive branch, enforce government policy, typically the head of the legislative majority party
eg. Keir Starmer of the United Kingdom, Mark Carney of Canada
Chancellor
-
The head of government, title has the same meaning as ‘Prime Minister’
-
Used by Germany, Austria, and Switzerland
eg. Olaf Scholz of Germany, Christian Stocker of Austria
General Secretary
-
The highest-ranking official in a political party, especially in communist or socialist states
-
Often hold supreme power
eg. Xi Jinping of the Chinese Communist Party, Kim Jong-un of the Workers’
Party of Korea (NPRK)
Chief Executive
-
The highest ranking official in a government entity
-
Responsible for overall management and decision-making
eg. John Lee Ka-chiu of Hong Kong
Branches of the Government
United States
United Kingdom
China
Major Political Departments
United States
Congress:
-
The department of the government which makes lawsThe Senate and the House of Representatives make up its two halves
House of Representatives:
-
A sector of Congress made up of 435 members
-
The number of representatives each state has depends on its population
-
They serve 2-year terms and make and vote on laws
Senate:
-
The other sector of Congress made up of 100 members - 2 from each state
-
Members serve 6-year terms
-
They vote on impeachment cases, and authorizes presidential appointments
Executive Branch:
→ The department of the government which carries out and enforces laws
→ Led by the President - also acting as the head of state and government
-
Supreme Court:
→ The highest court in the United States
→ Interprets and decides if laws and government actions comply with the constitution
United Kingdom
-
Parliament:
→ The department of the government which make laws
→ The Monarch (King or Queen), the House of Commons and the House of Lords
make up its three thirds
-
House of Commons:
→ A sector of parliament composed of 650 members who are elected by the people
→ Make and vote on laws, decide who will run the government
→ The Prime Minister is usually the leader of the party with the most members
-
House of Lords:
→ Another sector of parliament composed of members who are primarily appointed based on their accomplishments
→ These include nobles, senior judges, and church leaders
→ Review laws passed by the House of Commons but cannot entirely block them
-
Supreme Court:
→ The highest court in the country
→ It ensures that laws adhere to the constitution and renders final decisions on
important legal issues
-
Executive Branch:
→ The department which carries out and enforces laws
→ Involves the monarch, the Prime Minister and the Cabinet
→ Serves a constitutional monarchy - largely ceremonial role, with real political
power in the hands of the Prime Minister and Parliament
China
-
National People’s Congress:
→ The highest law-making body
→ Selects senior officials including the President and Premier, passes laws, and
authorizes significant decisions
→ Meets once a year, and the majority of its work is done by its Standing Committee while it is not in session
-
Supreme Court:
→ The highest court in the country
→ Renders decisions on important legal cases and significant court matters, ensures the law is properly applied
→ Governed by the NPC and the Communist Party, oversees subordinate courts
-
Central People’s Government:
→ Main government body which upholds the law and oversees government agencies
→ Headed by the premier and is supported by ministers and vice premiers
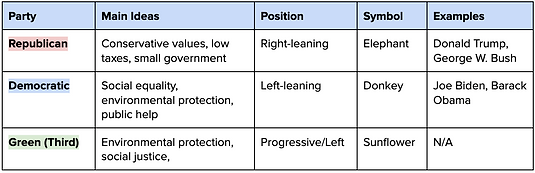
Political Parties
United States
United Kingdom
China
Political Theories
Democracy
Definition: A system of government where the people have the power to either vote directly on laws or elect representatives to make decisions for them.
Example: United States, United Kingdom, India
Republic
Definition: A form of government where officials are elected to represent the people, rather than a monarch.
Example: United States, France
Monarchy
Definition: A form of government with a king, queen or emperor as the head of state. They can be absolute (has total power and control) or constitutional (power is limited by a parliament or by law).
Example: United Kingdom (constitutional), Saudi Arabia (absolute)
Anarchy
Definition: A situation where there is no government or authority - often leading to chaos.
Example: Somalia experienced a period of anarchy after the collapse of its government in the early 1990s.
Liberalism
Definition: A theory emphasizing individual and equal rights, freedom, democracy, and free markets, which also supports limiting government power.
Example: Celebrated in many western countries, supported by the policies of countries including Germany and Canada.
Realism
Definition: A theory focused on power and the interests of the nation, acting to preserve a state’s own security rather than ideals.
Example: Realism explains much of the Cold War politics between the USA and the USSR in the mid to late-20th century.
Conservatism
Definition: A theory that favors gradual change over drastic reform while attempting to maintain traditional institutions, rituals, and values.
Example: The UK’s Conservative Party is a leading conservative political force.
Authoritarianism
Definition: A system in which power is in the hands of a single leader or a small group that exercises strong or absolute control over many aspects of life, often limiting political freedoms and opposition
Example: North Korea under Kim Jong-un, Nazi Germany under Adolf Hitler
Communism
Definition: An economic and political theory that strives toward a classless society where property is owned collectively and wealth is distributed equally. The state often controls production, output, and resources.
Example: The former USSR, Cuba, and China under Mao Zedong
Fascism
Definition: A nationalist, authoritarian government that prioritizes unity, a strong leader, and often suppresses opposition. It encourages centralized control and often militarism, while rejecting democracy.
Example: Nazi Germany under Adolf Hitler, Italy under Benito Mussolini
Socialism
Definition: A political and economic theory that aims to improve public welfare and reduce inequality by having the government or community own the means of production and distribution of goods.
Example: Nordic countries such as Sweden practice democratic socialism, Vietnam and Cuba represent modern socialist states, along with the former USSR
References:
-
Mission, U. S. (2022, June 30). Branches of the U.S. Government. How do they work? Branches of the U.S. Government. U.S. Embassy & Consulate in New Zealand, Cook Islands and Niue. https://nz.usembassy.gov/u-s-government/
-
The Branches of Government. (2025). Parl.ca. https://learn.parl.ca/understanding-comprendre/en/
-
Kwan, R. (2020, September 26). Explainer: Understanding Hong Kong’s debate around the separation of powers and an executive-led system. Hong Kong Free Press HKFP. https://hongkongfp.com/2020/09/26/
-
Separation of Powers. (2025). LII / Legal Information Institute. https://www.law.cornell.edu/wex/separation_of_powers_0
-
The three branches of government | Law Wales. (2021, March 16). Gov.wales. https://law.gov.wales/three-branches-government
-
Separation of Powers, Parliamentary Sovereignty & the Rule of Law | BIHR. (2025). British Institute of Human Rights. https://www.bihr.org.uk/get-informed/legislation-explainers/
-
Codings. (2025). CHINA’S STATE STRUCTURE AND THE TWO SESSIONS. Orcasia.org. https://www.orcasia.org/
-
China’s State Organizational Structure. (2012, August 29). CECC. https://www.cecc.gov/chinas-state-organizational-structure
-
About Congress | U.S. Capitol - Visitor Center. (2025). Visitthecapitol.gov. https://www.visitthecapitol.gov/explore/about-congress
-
The. (1998, July 20). Congress of the United States | Members, Seats, Term Length, & History. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/topic/Congress-of-the-United-States
-
The House Explained | house.gov. (2023). House.gov. https://www.house.gov/the-house-explained